A Dialogue
Bloggingheadstv
Science Saturday: The Recipe For Our Universe
Don't want to say to much other then to leave the images for consideration and relate them to what the dialogue is referring too.

Photo from NASA of the Bullet Cluster
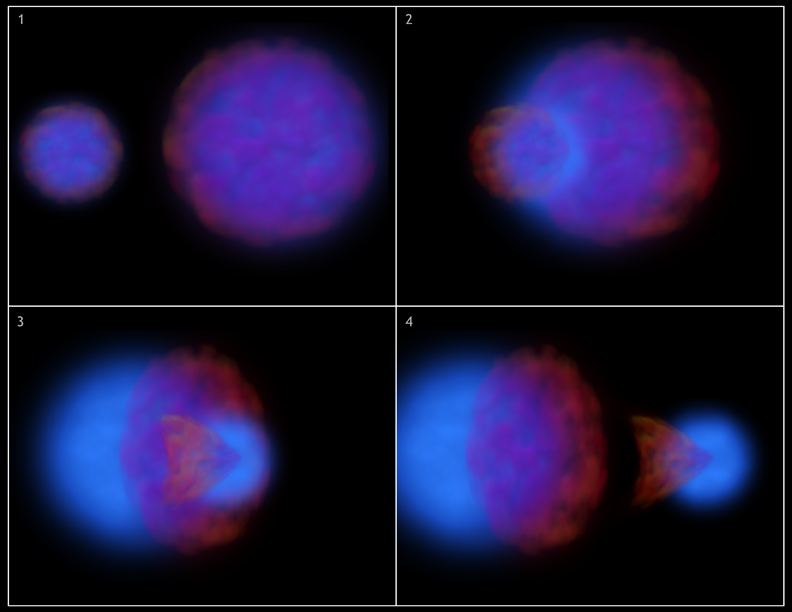
These stills show four stages from an artist's representation of the huge collision that is taking place in the bullet cluster. Hot gas, containing most of the normal matter in the cluster, is shown in red and dark matter is shown in blue. During the collision the hot gas in each cluster is slowed and distorted by a drag force, similar to air resistance. A bullet-shaped cloud of gas forms in one of the clusters. In contrast, the dark matter is not slowed by the impact because it does not interact directly with itself or the gas except through gravity. Therefore, the dark matter clumps from the two clusters move ahead of the hot gas, producing the separation of the dark and normal matter seen in the image. More Images
 What is Dark Matter? How Can We Make It in the Laboratory Conclusions
What is Dark Matter? How Can We Make It in the Laboratory Conclusions
Particle physics is in the midst of a great revolution. Modern data and ideas have challenged long-held beliefs about matter, energy, space and time. Observations have confirmed that 95 percent of the universe is made of dark energy and dark matter unlike any we have seen or touched in our most advanced experiments. Theorists have found a way to reconcile gravity with quantum physics, but at the price of postulating extra dimensions beyond the familiar four dimensions of space and time. As the magnitude of the current revolution becomes apparent, the science of particle physics has a clear path forward. The new data and ideas have not only challenged the old ways of thinking, they have also pointed to the steps required to make progress. Many advances are within reach of our current program; others are close at hand. We are extraordinarily fortunate to live in a time when the great questions are yielding a whole new level of understanding. We should seize the moment and embrace the challenges.
Lee Smolin:
"Here is a metaphor due to Eric Weinstein that I would have put in the book had I heard it before. Let us take a different twist on the landscape of theories and consider the landscape of possible ideas about post standard model or quantum gravity physics that have been proposed. Height is proportional to the number of things the theory gets right. Since we don’t have a convincing case for the right theory yet, that is a high peak somewhere off in the distance. The existing approaches are hills of various heights that may or may not be connected, across some ridges and high valleys to the real peak. We assume the landscape is covered by fog so we can’t see where the real peak is, we can only feel around and detect slopes and local maxima.
A counter perhaps to the Anthropic discussion?
 'An unexpected gift' from string theory
'An unexpected gift' from string theory
The possibility that enormously large galaxies originated from tiny quantum fluctuations may seem too strange to be true. But many aspects of inflationary theory were confirmed by recent astronomical observations, for which the observers won the Nobel Prize in 2006. This gives some credence to an even more surprising claim made by Linde: During inflation, quantum fluctuations can produce not only galaxies, but also new parts of the universe.
Take an expanding universe with its little pockets of heterogeneous quantum events. At some point one of those random events may actually "escape" from its parent universe, forming a new one, Linde said. To use the ball analogy, if it experiences small perturbations as it rolls, it might at some point roll over into the next valley, initiating a new inflationary process, he said.
"The string theorists predict that there are perhaps 101000 different types of universes that can be formed that way," Linde said. "I had known that there must be many different kinds of universes with different physical properties, but this huge number of different possibilities was an unexpected gift of string theory."
According to string theory, there are 10 dimensions. We live aware of four of them—three of space plus one of time. The rest are so small that we cannot experience them directly. In 2003, Stanford physicists Shamit Kachru, Renata Kallosh and Linde, with their collaborator Sandip Trivedi from India, discovered that these compacted dimensions want to expand, but that the time it would take for them to do so is beyond human comprehension. When a new universe buds off from its parent, the configuration of which dimensions remain small and which grow large determines the physical laws of that universe. In other words, an infinite number of worlds could exist with 101000 different types of physical laws operating among them. Susskind called this picture "the string theory landscape."
For many physicists, it is disturbing to think that the very laws and properties that are the essence of our world might only hold true as long as we remain in that world. "We always wanted to discover the theory of everything that would explain the unique properties of our world, and now we must adjust to the thought that many different worlds are possible," Linde said. But he sees an advantage in what some others could see a problem: "We finally learned that inflationary universe is not just a free lunch: It is an eternal feast where all possible dishes are served."


